Table of Contents
Thyroid Introduction
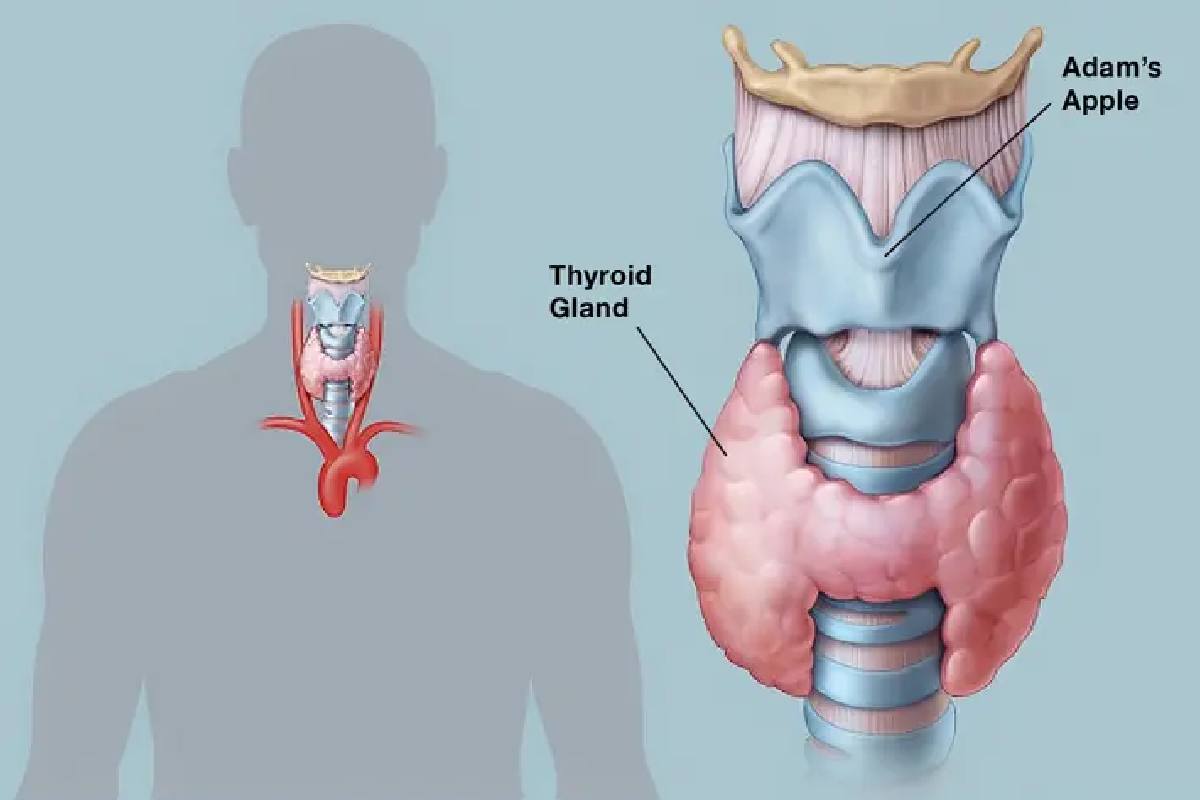
The thyroid is an endocrine gland which is in front part of the neck, and below adam’s apple. the thyroid has shape just like butterfly and its function is to provide hormones in whole body.
The hormones produced by the thyroid gland help control processes such as calorie consumption in the body the body’s metabolic rate and regulate the development of the body from birth to old age.
Function of Thyroid Gland
The main function of the thyroid gland is that it produce, store and release its hormones, called as T3The thyroid gland’s primary function remains to produce, store, and release it hormones, known as T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine), whose compound is thyroxine.
These hormones is responsible in developing the nervous system and balances the metabolism or the date in which body burns calories for energy.
These Hormones Are Responsible For:
- Monitor heart rate and cholesterol concentration
- Intervene in the synthesis of glycogen and the use of glucose
- form vitamin A
- Maintain body temperature
Have A Gastrointestinal Role Of Memory And Muscle Strength.
To perform all these functions, the thyroid is assisted by two other glands: the pituitary, responsible for identifying the number of thyroid hormones present in the blood and producing more if necessary (through the secretion of TSH); and the hypothalamus, which releases TRH so that the pituitary gland produces TSH.
Pathologies That Can Affect The Thyroid
Many diseases and disorders can affect the thyroid gland, usually causing it to over-or under-produce those hormones the body needs. It, in turn, can cause other problems in other regions.
Among The Problems That Can Affect The Thyroid Are:
Hyperthyroidism: Also known as an overactive thyroid, occurs when the gland produces excess it hormones. Excess hormones can cause many problems, including mood swings, anxiety, fatigue, and heart palpitations, to name just a few.
Hypothyroidism: Unlike hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism occurs when not enough it hormones are produced—causing symptoms such as constipation, feeling cold, tiredness. And difficulty concentrating. If a person suffers from hypothyroidism at a young age, this can cause growth problems, delayed puberty, and irregular menstrual periods.
Goiter: This term describes an enlarged it associated with a gland malfunction. It can cause symptoms like coughing, difficulty swallowing, and even breathing difficulties in some cases.
Thyroid Cancer: Like other organs and glands in the body, the gland is also susceptible to cancer. It is most common in women between 25 and 65 and Asian, although it can affect anyone.
Thyroiditis: This is the generic term for an inflamed thyroid. It can refer to several conditions, including Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, postpartum thyroiditis, and also, subacute thyroiditis. All these conditions affect different age groups and have other symptoms, although the inflammation of the it gland represents the common symptom.
Thyroid Disease Treatments
Treatment of a disorder varies depending on the type of condition. Medical specialists use your medical history, physical exam, and also, various tests to diagnose it disease. In some cases, a biopsy is also indicate.
Medications may be prescribe to correct the hormone levels produce by the gland, encourage more hormone production in hypothyroidism, or limit the number of hormones produced in hyperthyroidism.
If surgery is require, this usually involves removing part of the gland or removing the swelling or goiter. However, surgical treatment for patients with thyroid cancer is booming, and many patients make a full recovery when the cancer is diagnose early.