Brain tumor can affect brain function if they grow large enough to pressure surrounding nerves, blood vessels, and tissue. Your outcome will be determined by factors such as the type, grade, and location of the tumor; success of tumor removal; and your age and general health.
Table of Contents
What Is A Brain Tumor?
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth or mass of cells in or around the brain. It is also known as a central nervous system tumor.
Brain tumors can be nasty cancer or benign non-cancer. Some tumors multiply; others grow slowly.
Only about a third of brain tumors are malignant. However, whether cancerous or not, brain tumors can impair brain function if they grow large enough to pressure surrounding nerves, blood vessels and tissue.
Tumors that grow in the brain are called primary tumors. Tumors that spread to the brain after starting in another part of the body are secondary or metastatic. This object focuses on primary tumors. There are extra than 100 types of primary brain and spinal cord tumors.
How Common Are Brain Tumor?
Doctors diagnose brain tumors in approximately 85,000 people in the United States each year. Of these tumors, about 60,000 are benign and about 25,000 are malignant.
Who Is Affected By Brain Tumor?
Brain tumors are more mutual in men than in women. Though they are more mutual in older people, they can develop at any age. Brain tumors are the vital cause of cancer-related death in children under 14.
What Types Of Brain Tumors Are There?
Doctors classify brain and central nervous system tumor based on their start and the type of cells they affect.
Typically Benign Brain Tumors Include:
Acoustic neuroma: These tumors occur on the vestibular nerve (the nerve that runs from the inner ear to the brain). Acoustic neuromas are also call vestibular schwannomas.
Gangliocytoma: These vital nervous system tumors form in neurons (nerve cells).
Meningioma: This is the common record type of primary . Meningiomas grow slowly. They form in the meninges, the coatings of skin that protect the brain and spinal cord. In occasional cases, a meningioma can be malignant.
Pineocytoma: These slow-growing tumors procedure in the pineal gland, which lies deep in the brain and secretes the melatonin hormone.
Pituitary adenoma: These tumors system in the pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland crops and controls hormones in the body. Pituitary adenomas are usually very small.
Chordoma: These slow-growing tumors usually start at the base of the skull and lower spine. They are generally benign (non-cancerous).
What Causes A Brain Tumor?
Doctors don’t know precisely what causes most brain tumors. However, mutations (changes) or defects in genes can cause brain cells to grow out of control and lead to a tumor.
The only known environmental cause of brain tumor is exposure to large amounts of radiation from x-rays or previous cancer treatments. In addition, some brain tumors arise when inherited diseases are passed down between family members.
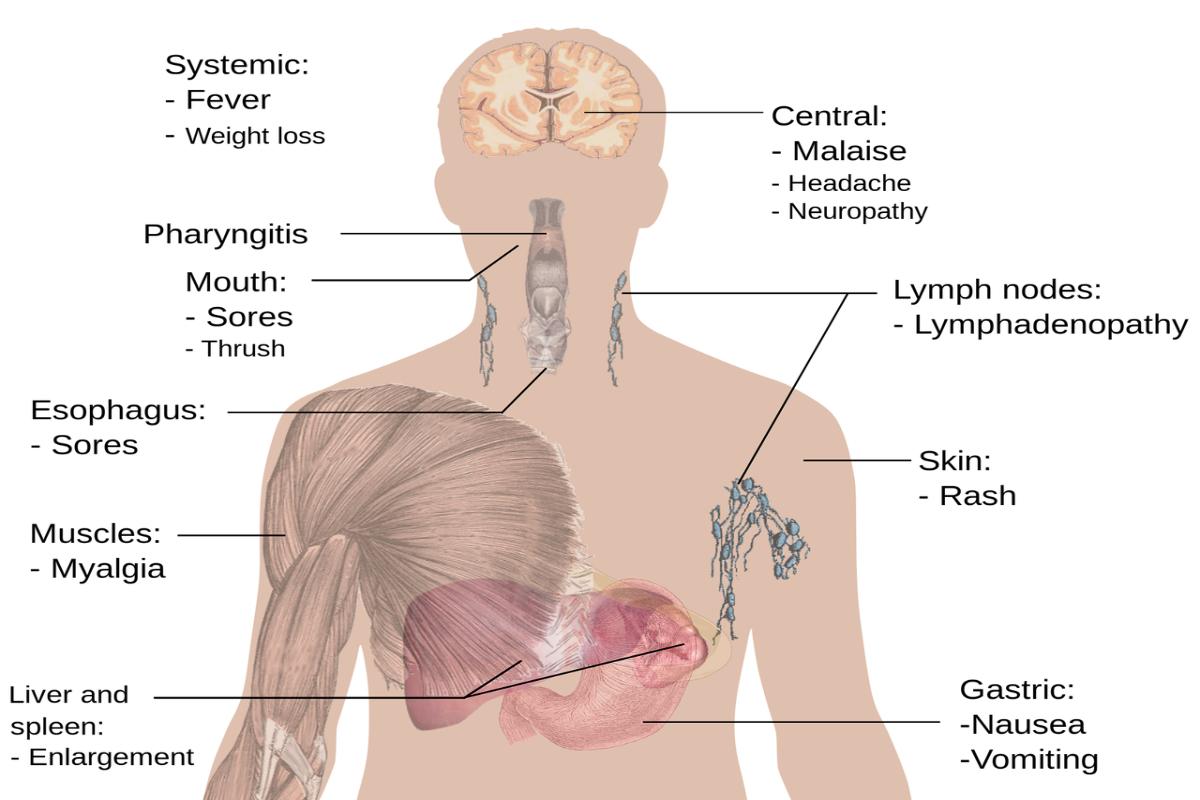
Symptoms Of A Brain Tumor
Some people with brain or central nervous system tumor have no symptoms. However, doctors find a tumor while treating another problem in some cases.
When a brain tumor grows and presses on nearby nerves or blood vessels, it can cause symptoms. The signs and symptoms of a vary depending on the location and type of tumor, its size, and what controls the affected part of the brain. This may include:
- Continuous or severe headaches appear in the morning or disappear after vomiting.
- Behavioral or personality changes.
- Difficulties with balance or coordination.
- Difficulty concentrating.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Coldness, weakness or tingling in one part or side of the body or face.
- Hearing, sight or vision problems
- Also Read: infinate fidgets com